
As Cohen ( 1988) writes, “The Z subscript is used to emphasize the fact that our raw score unit is no longer X or Y, but Z,” where Z are the difference scores of X-Y. If we want to perform an a-priori power analysis, we are asked to fill in the effect size dz. To illustrate the effect of correated observations, we start by simulating data for a medium effect size for a dependent (or paired, or within-subject) t-test. 15.8.1 Reproducing Brysbaert Variation 1: Changing Correlation.Appendix 2: Direct Comparison to MOREpower.Appendix 1: Direct Comparison to pwr2ppl.15.3 Conclusion on a Binary RCT with Interim Analyses.15.2 Binary RCT with a Interim Analysis.15.1.5 Conclusions on the Binary RCT Analysis.15.1.2 Step 1: Create a Data Generating Function.
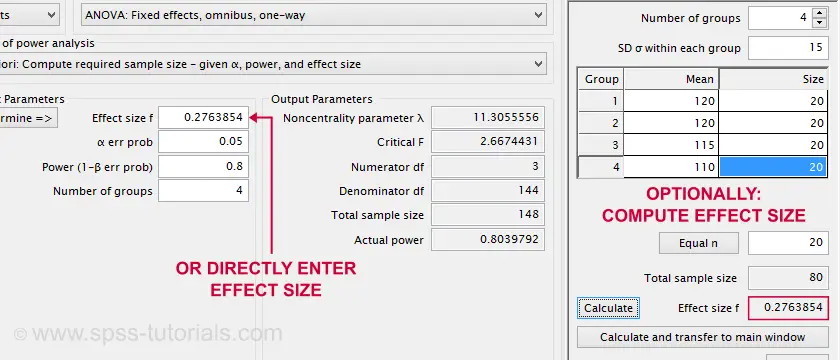
GPOWER TO CALCULATE EFFECT SIZE TRIAL
15.1 A Clincal Trial with a Binary Outcome.15 Beyond Superpower II: Custom Simulations.14 Beyond Superpower I: Mixed Models with simr.13.4 Equivalence and non-superiority/-inferiority tests.12.2.1 MANOVA or Sphericity Adjustment?.12.2 Violation of the sphericity assumption.12.1 Violation of Heterogeneity Assumption.
GPOWER TO CALCULATE EFFECT SIZE CODE


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
